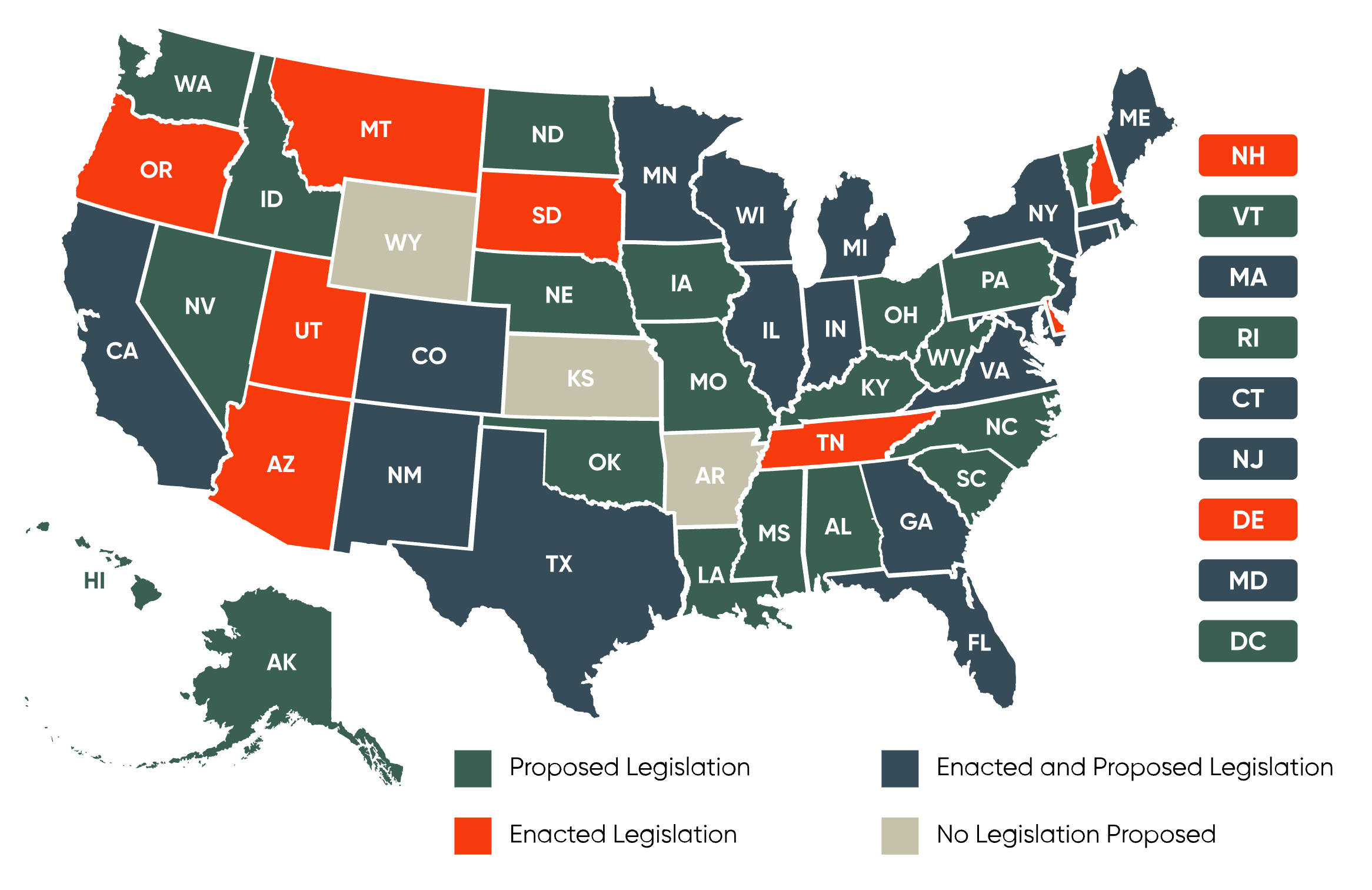
State-Level AI Legislation in 2025: A Closer Look
The past few years have seen states across the nation take on the tricky parts of artificial intelligence regulation. In 2025, policymakers have been busy crafting laws to address issues ranging from nonconsensual imagery and election interference to automated decision-making and government use of AI. This opinion editorial offers an in-depth overview of how state legislators are coping with these tangled issues, bringing forward a mix of bipartisan consensus and serious differences in approach.
At a time when AI developments are both promising and nerve-racking, state lawmakers recognize the need to protect citizens while understanding that too much regulation might stifle innovation. With federal oversight looming in the background, states seem determined to take control of local AI regulation, even as their efforts risk being derailed by nationwide debates on the subject.
Understanding the Current US AI Legislative Landscape
At its core, the state-level AI legislative push reflects both a reaction to the potential harm of unchecked technology and an attempt to craft rules that foster responsible innovation. With bipartisan interest emerging on specific themes such as nonconsensual intimate imagery (NCII) and election-related tactics, the landscape is as complicated as it is vibrant.
Key findings from recent data indicate:
- Approximately 260 AI-related measures were introduced in the 2025 legislative session.
- Of these, 22 have been passed while many others are pending or have died in committee.
- Two-thirds of the proposed measures originated from Democratic lawmakers, with Republican legislators focusing on both protective bans and promoting innovation-friendly policies.
This data paints a picture of a fragmented yet determined effort across states to respond to AI's expanding role, all while managing the subtle details and tricky parts of the potential consequences.
Bipartisan Movements and Diverging Priorities
One notable trend in state AI regulation is the stark contrast between efforts led by Democrats and those by Republicans. While Democrats have favored broader regulatory bills targeting sweeping oversight for AI developers and government use, Republicans have typically promoted approaches that emphasize limiting harmful applications without overly burdening technology creators.
For instance, some states have pushed for stringent measures that impose obligations on AI developers to provide transparency or secure human oversight. Others have preferred lighter-touch policies that rely on market self-regulation. These contrasting strategies are manifested in various proposals, including:
- Bipartisan efforts: A few states, such as Minnesota, New Jersey, and Tennessee, have managed to rally cross-party consensus on issues like election deepfake bans and child pornography regulations.
- Republican-led initiatives: Some states, like Texas, have focused on narrowly defined bans with fewer rules on broader accountability, although many of these proposals have not advanced significantly.
- Democratic-led measures: States such as California, New York, and New Jersey have introduced bills demanding comprehensive disclosures and strict rules for AI systems, especially in areas considered high-risk.
Ultimately, the political alignment of the proposals signals that while there is a super important common ground on preventing clear harms, different political groups are interpreting the fine points of AI oversight in varied ways.
Addressing Nonconsensual Intimate Imagery and Child Sexual Abuse Material
One of the most pressing concerns that state lawmakers are tackling is the misuse of AI to create nonconsensual intimate imagery (NCII) and child sexual abuse material (CSAM). In numerous instances, legislators have tried to address these issues through take-it-down approaches that impose heavy penalties on platforms and individuals responsible for disseminating such content.
A Maryland bill, for example, mandates that certain online platforms establish clear methods for individuals to request the removal of nonconsensual imagery, including synthetic versions. Similarly, Mississippi introduced a measure making the creation or dissemination of harmful deepfakes with an intent to cause injury a punishable offense. Across at least 16 states, proposals have emerged that target NCII and CSAM—although many of these measures have stalled in committee.
The following table summarizes key aspects of these proposals:
| Issue | Number of Bills Introduced | Status |
|---|---|---|
| NCII/CSAM | 53 | None signed into law |
| Election Interference (Deepfake-related) | 33 | None signed into law |
These legislative initiatives underscore a shared commitment to protect individuals from the overwhelming, often nerve-racking misuse of AI in sensitive areas. What remains under discussion, however, is how to balance the need for freedom of expression with the undeniable harm that synthetic content can inflict on personal and social levels.
Election Integrity and AI: A Balancing Act
Another facet of state-level AI legislation focuses on the role that AI plays in election-related matters. In recent sessions, many bills have been introduced to ensure that political communications remain transparent, especially in the age of deepfakes and synthetic media.
For example, a New York proposal requires political candidates to disclose when they have used AI to craft advertising content. Another measure from Massachusetts targets the creation and dissemination of deepfake videos or altered images by setting a specific time threshold—90 days before an election—as a critical period for regulation.
These proposals highlight the need to protect democratic processes without stifling political innovation. The challenge here is twofold:
- Transparency: Voters must be clearly informed if AI is employed to influence political opinion.
- Fairness: Both political parties should adhere to the same rules when using or being targeted by AI-generated content.
Despite bipartisan interest, many of these election-related bills have not yet advanced beyond committee stages. Lawmakers continue to grapple with the nerve-racking prospect of either over-regulating political speech or leaving the door open for harmful manipulation.
Ensuring Transparency in Generative AI Communications
With the rise of conversational agents and chatbots that can mimic human behavior, state legislatures have also concentrated on generative AI transparency. The crux of these proposals is that consumers have the right to know when they are engaging with an automated system rather than an actual human representative.
In Hawaii, for instance, a bill requires that any entity engaging in commercial transactions explicitly inform consumers if they are interacting with a chatbot or similar technology. Massachusetts has proposed similar initiatives. These measures require organizations to take proactive steps, such as:
- Clearly labeling interactions with digital assistants.
- Establishing a red team to test the resilience of any digital watermarks used to identify AI-generated content.
- Reporting their findings to state authorities.
Both Hawaii and New Mexico saw their bills in this area fizzle out on the legislative floor, while Massachusetts continues to work through its committee. The state-level push for transparency is crucial, given the overwhelming possibility of consumers being misled by technology that is designed to be human-like.
Managing Automated Decision-Making and High-Risk AI
Legislation addressing automated decision-making technologies and so-called high-risk AI systems is at the forefront of many state initiatives. Borrowing heavily from Colorado’s early lead with its comprehensive AI Act, states like Georgia, Illinois, Iowa, and Maryland have sought to enforce strict guidelines ensuring that AI's role in consequential decision-making is both transparent and controlled.
The core components of these proposals include:
- Prevention of algorithmic discrimination.
- Public disclosure of AI involvement in important decisions.
- Mandating that AI developers and deployers implement measures to address potential biases or errors.
- Providing consumers with an explanation whenever AI is a significant factor in decisions that affect them.
While Colorado’s legislation is set to go into effect in 2026, similar bills in other states are struggling with the same nerve-racking challenges of defining “high-risk” systems and balancing regulatory measures with the freedom to innovate. Although Georgia, Iowa, and Maryland saw their proposals stall in committee processes, the efforts represent a critical step toward understanding the subtle details of AI's role in our everyday lives.
Government Use of AI: Ensuring Accountability and Transparency
Another key area under legislative scrutiny is the use of AI by government entities. From ensuring accountability to mandating human oversight, state bills aim to protect citizens from potentially harmful decisions made by automated systems in the public sector.
For example, a bill in Georgia seeks to create an AI Accountability Board, which would require state agencies to develop clear AI usage plans covering specific goals, data privacy measures, and human oversight processes. In contrast, Montana has taken a more restrictive stance by limiting the use of AI in state and local government actions outright, demanding transparency regarding when AI systems are involved in decision-making processes.
Additional proposals in states like Nevada require departments such as the Department of Taxation to notify citizens if their communications might be handled by AI. These legislative efforts focus on two main issues:
- Oversight: Ensuring that any decision made using AI is subject to human review.
- Disclosure: Making sure that citizens are aware when AI systems are part of the decision-making process.
Although several bills in this area have died in committee, their existence reflects a growing discomfort with the idea of unaccountable governmental reliance on AI technologies.
Protecting Employee Rights in an AI-Driven Workplace
Another critical front in the battle over AI regulation is employment. States are increasingly considering bills designed to shield employees from the unpredictable twists and turns of AI in workplace decision-making. These proposals are typically aimed at ensuring that job applicants and current employees are fully informed when AI-based systems are involved in hiring, promotion, or performance monitoring.
For example, an Illinois bill—currently sitting in the assignments committee—requires employers to notify applicants if AI plays any part in the interview or decision-making process. Similarly, Pennsylvania has seen discussions on comparable measures. In California, lawmakers are pushing forward bills aimed at limiting excessive AI-based workplace surveillance.
Key concerns in this area include:
- Protection against biased or opaque hiring algorithms.
- Ensuring transparency around AI's role in evaluating employee performance.
- Maintaining a human element in personnel decisions to prevent overwhelming reliance on automated systems.
These employment-related initiatives, though still evolving, point to the need to balance innovation with the preservation of fair labor practices. As employers increasingly adopt digital means for recruiter functions, the new regulations may soon become a must-have for maintaining trust and fairness in the workplace.
The Intersection of AI and Health: A Delicate Balance
Health care represents one of the sectors where the stakes of AI regulation are particularly high. State legislation in 2025 has sought to address how AI systems are used in both treatment and administrative processes. The goal here is to prevent any harmful ramifications resulting from automated decision-making in a field where human health is directly at risk.
For instance, a bill in California prohibits the use of certain terms or phrasing that might imply a health care professional’s AI-generated recommendations have been approved by a licensed expert. In Illinois, another proposal awaiting the governor's signature would ban licensed health care professionals from relying on AI to make therapeutic decisions or generate treatment strategies. Meanwhile, Indiana has introduced measures that require health care providers and insurers to notify patients when AI is involved in their care.
These legislative proposals in the health care arena pivot around critical elements such as:
- Patient Awareness: Making sure that patients are fully informed about the use of AI in diagnostic and treatment decisions.
- Professional Integrity: Ensuring that health care professionals maintain the final decision-making authority in all patient care processes.
- Data Privacy: Protecting sensitive patient data while allowing for innovation in health care delivery.
The health care bills are emblematic of the broader state-level effort to address the hidden complexities and subtle details of integrating AI into sensitive, life-impacting areas. With patient well-being at the forefront, lawmakers are carefully working through an approach that minimizes risk without completely shutting down technological progress.
Key Challenges and Confusing Bits in State AI Regulation
Though the proliferation of state-level proposals demonstrates a clear determination to address AI’s impact, the process is not without its confusing bits and tangled issues. Several challenges stand out in the current legislative environment:
- Diverse Priorities: Differing approaches between states lead to a patchwork of regulations that might confuse both businesses and consumers. While some states are adopting comprehensive regulatory frameworks, others are opting for more narrow, sector-specific bills.
- Committee Roadblocks: Many promising bills have met with early resistance in committee stages, where concerns over unintended consequences or overly stringent regulation have stalled progress.
- Federal Overlap: With discussions at the national level about a potential moratorium or federal oversight of state legislation, there is an ongoing debate regarding the appropriate balance between local control and nationwide uniformity.
- Complex Policy Tradeoffs: Lawmakers struggle to balance protecting citizens from the intimidating consequences of misused AI and preserving the innovation that drives economic growth and societal betterment.
In summary, while states are eager to tackle the major themes associated with AI, the journey is full of twists and turns. Lawmakers must figure a path through a maze of competing interests and potential pitfalls before arriving at effective regulations that benefit everyone.
Future Directions: How States Can Chart a Successful Course in AI Regulation
Even as states work to regulate AI in a piecemeal fashion, there is hope that some lessons learned from earlier initiatives can pave the way for a more coherent national strategy. Here are several key strategies that could help state legislators and policymakers steer through the evolving AI landscape:
- Adopt a Consortium Model: States might consider forming partnerships with academic institutions, tech companies, and international partners to share expertise and develop best practices for AI governance.
- Focus on Talent Development: Initiatives such as the "Computer Science For All Act" emphasize the need for a well-prepared workforce capable of handling advanced AI technologies. This would ensure that both policy implementation and technical oversight are well-informed by the latest advancements.
- Create Flexible Regulatory Frameworks: Given that AI technology is still maturing, it may be beneficial to design regulations that can adapt to new developments. A flexible approach could balance the need for quick action and the ability to update rules as technology evolves.
- Encourage Transparency and Accountability in Government Use: Establishing dedicated oversight boards or accountability frameworks for governmental AI use can promote public trust and ensure that the human review remains central in critical decision-making processes.
- Engage Stakeholders Early and Often: Continuous dialogue between legislators, technologists, civil society, and industry stakeholders can help uncover subtle parts and hidden complexities early on in the regulatory process. This inclusive approach can mitigate the risk of overly restrictive or ineffective laws.
Implementing these strategies could not only help states manage the tricky parts of AI legislation but also create a cohesive model that might inform future federal policies. The overall goal remains to protect citizens while leaving room for innovation—a balance that is as challenging as it is critical.
Comparing State Initiatives: A Snapshot of Legislative Variations
A helpful way to appreciate the diverse approaches taken by states is to compare some of the standout initiatives side by side. The table below illustrates the differences in focus and legislative status among various states:
| State | Focus Area | Key Requirements | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maryland | NCII/CSAM | Take-it-down procedure for synthetic imagery | Pending/Committee |
| New York | Election Transparency | Disclosure of AI involvement in campaign ads | Under Consideration |
| Colorado | High-Risk AI | Transparency in consequential decisions, anti-discrimination measures | Law |
| Georgia | Government Use | Establishment of an AI Accountability Board | Proposed / Died in Committee |
| California | Health & Employment | Restrictions on AI-based healthcare advice and workplace surveillance | Various committees |
This snapshot reveals a patchwork regulatory environment that is as diverse as it is experimental. While no single model has yet emerged as the definitive solution, the differences between states underscore the need for policymakers to figure a path forward carefully, weighing both the beneficial potential and the possible dangers of AI.
Federal Influence: A Storm Cloud on the Horizon?
While state legislatures continue to take measures to address AI, there is growing concern over possible federal actions that could upend these local efforts. Recent discussions in the U.S. Senate about implementing a 10-year moratorium on state AI regulations have sparked heated debates. Although the proposal was eventually dropped, its mere introduction indicates that federal lawmakers are keeping a close watch on state-level progress.
Key aspects of the federal debate include:
- Standardization vs. Flexibility: Federal regulators may favor a uniform set of laws that apply nationwide, which could simplify the legal landscape but might also ignore the local subtleties that need tailored solutions.
- Oversight and Enforcement: A federal framework might establish central agencies or guidelines that could either support state efforts or significantly restrict local autonomy in shaping AI policies.
- Balancing Innovation and Protection: As the federal government monitors state legislation through initiatives like the AI Action Plan, there is an ongoing need to support innovation while ensuring that citizens are shielded from harmful practices.
This potential for federal intervention casts a long shadow over state initiatives. Lawmakers must now not only work through the nerve-racking twists and turns within their own legislative processes but also prepare for possible preemption by national standards. In this environment, collaboration and dialogue between state and federal policymakers become even more important.
Lessons from the Past and a Look to the Future
Historically, the rapid evolution of technology has always forced regulators to catch up with innovation. The early days of the internet, for example, were marked by a wide disparity in state laws until more uniform regulations eventually took shape. Today, as AI continues to evolve at a breakneck pace, state legislators are taking the wheel on a new frontier.
Some key takeaways that can help guide future efforts include:
- Adapting to Change: The legal community must be prepared for the overwhelming and often nerve-racking pace of technological innovation, ensuring that laws remain relevant and flexible.
- Collaborative Policymaking: Engaging with stakeholders from technology, academia, and civil society can help lawmakers dig into the fine points and little details that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Protecting Fundamental Rights: Whether addressing issues of privacy, election integrity, or health care, the overriding goal remains to protect citizens from the unintended consequences of AI without stifling progress.
- Continued Experimentation: As states pilot diverse approaches, comparative analyses will be invaluable in identifying best practices and crafting policies that could serve as models for a broader national framework.
In conclusion, the journey of regulating AI at the state level is both innovative and complex, filled with overwhelming challenges and exciting opportunities. As states experiment with different legislative approaches—from piecemeal measures to comprehensive regulatory frameworks—the overall picture remains one of a nation on the brink of significant change.
Concluding Thoughts: Steering Through the Uncertain Future of AI Regulation
It is clear that state lawmakers are beginning to figure a path through the winding, sometimes intimidating labyrinth of AI regulation. By focusing on key areas such as NCII/CSAM, election integrity, transparency in generative AI, high-risk automated systems, government use, employment, and health care, states are addressing both the critical and subtle parts of this broad challenge.
Though many bills are still working their way through committee halls, the underlying commitment is evident: protecting citizens from the potential harms of technology while striving to leave room for innovation. As states continue to press forward, the numerous proposals serve as a testament to the nation’s dedication to safeguarding its people—even if the journey is full of confusing bits and soft, subtle differences that require continuous rethinking.
Looking ahead, it is imperative that legislators at state and federal levels collaborate more closely. By learning from experiments in different states and engaging in ongoing dialogue with experts and community stakeholders, regulators can create a robust framework that prevents abuse while fostering the benefits of AI.
The next few years promise to be a nerve-racking yet exciting period for AI legislation. With the federal government closely monitoring state efforts and potential preemption always on the horizon, lawmakers must remain agile, responsive, and innovative. The success of state-led initiatives will not only shape local policies but also have far-reaching impacts on the national AI regulatory agenda.
As we take a closer look at the future, one thing remains certain: artificial intelligence, with all its promise and perils, will continue to transform society. Crafting effective legal responses in this evolving landscape is not just a matter of regulation—it is a vital step in ensuring that technology works for the benefit of all citizens.
In the spirit of progress, it is essential for all stakeholders—policy experts, legal professionals, technologists, and the general public—to stay informed, engaged, and proactive in adapting to the ever-changing reality of AI governance.
This editorial is part of an ongoing series aimed at shedding light on state-level AI regulation efforts and offering insights into how best to manage the unpredictable and sometimes overwhelming challenges posed by artificial intelligence. Through these discussions, our hope is to steer the conversation toward balanced, effective solutions that protect individual rights and promote innovation at the same time.
Originally Post From https://www.brookings.edu/articles/how-different-states-are-approaching-ai/
Read more about this topic at
States Can Continue Regulating AI—For Now | Brownstein
US state-by-state AI legislation snapshot








No comments:
Post a Comment