State-by-State Legal Maze: The Tangled Issues of Sexual Education in American Schools
Across the United States, sexual education in public schools has become a subject loaded with tension and on edge debates. Recent research from Boston University School of Public Health highlights how inconsistent, outdated, and politically charged state mandates result in a confusing patchwork that may leave many students without the essential information needed to make informed decisions about their sexual health, relationships, and overall well-being.
No federal law compels schools to provide sexual education; instead, decisions are made at the state and local levels, leading to a landscape where policies vary widely. This op-ed takes a closer look at the state-by-state legal maze, the subtle parts of curricula regulation, and suggests ways to promote a more comprehensive, medically accurate approach for young people.
Overview of Current Mandates in Sexual Education
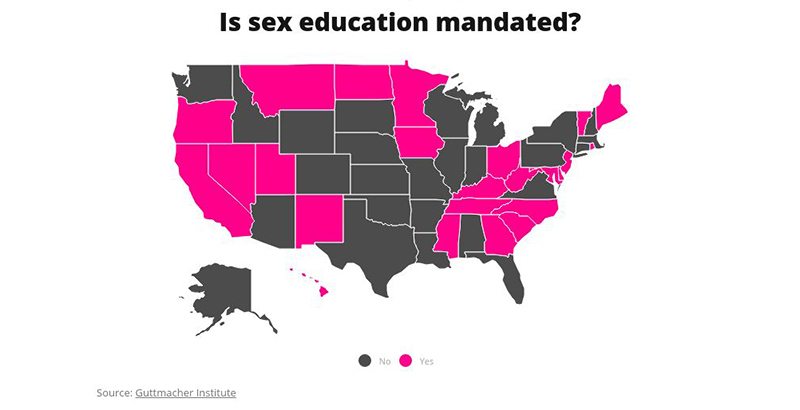
A recent study has found that 42 states require public school students—from kindergarten through high school—to participate in sexual education courses covering at least one topic related to sexual health. However, only 19 states require that instruction be medically accurate, with 5 of those states mandating accuracy on only certain topics. This disparity illustrates the tangled issues inherent in state-level mandates and raises substantial concerns for educators, parents, and lawmakers seeking to safeguard adolescent health.
The study’s findings underscore the notion that while many students are technically receiving some form of sexual education, few are likely to benefit from a comprehensive or scientifically sound curriculum. With many states requiring early and often ineffective abstinence-only education, the current legal framework delivered by public schools falls short of the needs of a diverse student body.
Exploring the Controversial Landscape of Curriculum Requirements
When it comes to drafting curriculum requirements, state laws have not only become politically motivated but also influenced by parent opt-out and opt-in policies. In 34 states, abstinence is a mandated component; despite significant evidence suggesting that abstinence-only methods can be intimidating and ineffective, these policies continue to form the backbone of many sexual education programs. Supporters of abstinence-only policies argue that such an approach fits their moral and cultural outlooks, yet critics insist these methods are both off-putting and incomplete.
Moreover, the regulations concerning parental consent or opt-out provisions add another layer of complication. In some states, parents must actively opt in if they want their children to receive instruction on sexual health topics, while in as many as 34 states, parents are allowed to opt their children out entirely from receiving any sexual education. This creates a scenario in which political compromises lead to a fragmented approach wherein many students may not be exposed to medically accurate and inclusive information.
The Fine Points of Regional Policy Variation
A dive into the state-by-state details reveals significant regional disparities. For example, every state in the Northeast mandates at least one topic in sexual education. In contrast, while 88 percent of states in the South, 83 percent in the Midwest, and only 62 percent in the West have such mandates, this variation shows how local sociopolitical forces and cultural values shape the educational experience. Each region’s unique take on sex ed curriculum opens up a host of confusing bits and subtle parts that require careful reading to truly get a clear picture.
The regional differences may also be illustrated by a simple table:
| Region | Percentage of States with Mandated Sexual Education |
|---|---|
| Northeast | 100% |
| South | 88% |
| Midwest | 83% |
| West | 62% |
This table simplifies the picture, but it does not fully capture the nerve-racking twists and turns in policy implementation. Each state’s statute, administrative regulation, and even court decisions add layers of confusing bits that educators and lawmakers must figure a path through.
Debating Medically Accurate Versus Politically Driven Instruction
A particularly nagging issue revealed by the study is the discrepancy between the need for medically accurate sexual education and the political pressures that lead to curricula filled with inaccuracies and outdated concepts. Only 19 states mandate medically accurate instruction, meaning that large numbers of adolescents are left with content that may not reflect the latest research or public health guidance.
Key points in this debate include:
- Abstinence-Only Emphasis: In 34 states, the law mandates instruction on abstinence as the primary method of sexual health education. Despite mounting evidence that an exclusive focus on abstinence can be both overwhelming and counterproductive, the tradition of abstinence-only education persists.
- Limited Scope of Topics Covered: While some states cover a range of subjects like HIV, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), child abuse prevention, and even healthy relationships, only 20 states require instruction on contraception and very few cover topics like sexual orientation, consent, or condom use.
- Stigmatizing Language: In some cases, states such as Oklahoma and Texas have been reported to include messaging that attaches a negative stigma to same-sex activity, a practice that undermines efforts to create inclusive learning environments.
These political pressures and varying mandates pose nerve-racking challenges for policymakers who aim to provide clear, medically sound information while also addressing the concerns of different political and cultural groups.
Legal Implications and Constitutional Considerations
From a legal standpoint, the absence of a federal mandate on sexual education means that constitutional and state-level rights collide in complicated ways. With education traditionally falling under state jurisdiction, the balance between parental rights and the state’s duty to equip students with the information they need is a key battleground.
Key legal implications include:
- State Authority: Each state’s legislature exercises considerable power in shaping sexual education policies. Some lawmakers argue that these decisions reflect local values, while activist groups contend that such patchwork laws put students at risk.
- Parental Rights: Policies that require parental opt-in or allow opt-out provisions generate significant legal debates. Legal experts are divided on whether these measures are protective or if they inadvertently leave students insufficiently informed.
- Equal Protection Issues: Uneven educational standards across jurisdictions might result in unequal protection under the law. Adolescents in one state could have access to medically accurate, comprehensive education while their peers in another state might not.
Constitutional arguments have been raised about whether the lack of a unified federal approach violates adolescents' rights or fails to meet the state's responsibility in supporting public health. As lawmakers continue to sort out these issues, the legal framework remains a tangle of state discretion, parental control, and individual rights.
Assessing the Impact on Adolescents’ Health and Well-being
The gaps in sexual education have a direct impact on adolescent health, influencing decisions that can affect them for life. Studies have shown that comprehensive, medically accurate sexual education can help reduce rates of STIs, unwanted pregnancies, and risky behaviors. However, when students receive incomplete or outdated instruction, they are less likely to make informed, healthy decisions—placing them at a disadvantage in both personal and public health realms.
Adolescents face an array of health risks that include:
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Inadequate education means students may not understand how to protect themselves effectively.
- HIV/AIDS Knowledge Gaps: Without proper instruction on prevention and treatment, misconceptions can persist, causing long-term harm.
- Increased Unwanted Pregnancies: Limited information regarding contraception and reproductive health leaves many without the tools to prevent unintended pregnancies.
- Poor Understanding of Consent and Healthy Relationships: Without clear guidance on the little details of consent, students may struggle to establish the boundaries necessary for healthy interpersonal relationships.
A significant concern is how uneven implementation of these programs can perpetuate inequality. Students in jurisdictions with comprehensive sexual education are far better positioned to make smart, healthy choices compared to those left with a curriculum that is both politically skewed and clinically outdated.
Working Through the Challenges of Parental Involvement Policies
One of the confusing bits in the overall policy matrix is the varying role parental involvement plays in shaping sexual education outcomes. In many states, parents hold substantial sway over what their children are taught. Some of the key points of tension include:
- Opt-Out Policies: In 34 states, parents have the right to remove their children from sexual education classes entirely. While this might seem like a protective measure, it can leave students with little to no exposure to critical health information.
- Opt-In Mandates: Conversely, five states require explicit parental consent before children can receive any sexual education. This creates an additional, nerve-racking hurdle for ensuring that all students benefit from these lessons.
- Curricular Review Provisions: Some jurisdictions allow parents to review curriculum materials in advance. While this may reassure some families, it can also pave the way for politically motivated censorship or dilution of important content.
These policies exemplify the balance lawmakers hope to strike: protecting parental rights while ensuring that young people receive the key information necessary to navigate their health and relationships. Unfortunately, the compromises required by permissive parental control tend to weaken the overall educational mission.
Examining the Role of Politically Influenced Messaging in Curriculum Content
Political agendas have a powerful influence on what topics are taught in schools, and this is especially true in the realm of sexual education. The enforcement of abstinence-only policies in 34 states illustrates how political preference sometimes takes center stage over medically derived facts. Such messaging not only distorts the facts but may also promote a framework that is both intimidating and, in some cases, off-putting to students seeking clear guidance.
Some controversial aspects include:
- Promotion of Single-Strategy Messaging: The heavy emphasis on abstinence disregards the broader array of methods available for protecting one’s health. A more layered approach—one that includes discussions about contraception, consent, and healthy relationships—would better serve students in managing their sexual health.
- Use of Stigmatizing Language: Certain state mandates have been observed to include negative messaging about sexual orientation or same-sex activities. This not only alienates LGBTQ+ students but also sends a damaging message about inclusivity in sexual education.
- Outdated Information: The persistence of curricula using techniques that are known to be ineffective highlights the slow pace of adaptation to current scientific insights and best practices in sexual health instruction.
These politically driven messages illustrate the little twists involved in shaping sexual education and demonstrate how educational content can be manipulated to serve broader, sometimes partisan, agendas rather than the well-being of students.
Comprehensive Versus Fragmented Sexual Education: A Comparative Analysis
A look at the complete picture reveals stark contrasts between jurisdictions that strive for comprehensive sexual education and those that allow a fragmented approach:
- Comprehensive Programs: These typically include medically accurate content on abstinence as well as contraception, sexually transmitted infections, consent, and healthy relationships. Importantly, such programs incorporate guidance that encourages open-mindedness and the development of critical thinking skills among adolescents.
- Fragmented Programs: In several states, the curriculum focuses narrowly on abstinence or selective topics, often leaving significant gaps in students’ understanding. This fragmented approach fails to manage your way through the full range of issues that teenagers need to explore in order to make healthy, informed decisions.
A simple comparison can be illustrated in the table below:
| Aspect | Comprehensive Sexual Education | Fragmented Sexual Education |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage of Topics | Abstinence, contraception, STIs, consent, healthy relationships | Primarily abstinence, limited contraception and inadequate emphasis on consent |
| Medical Accuracy | Based on updated, medically verified content | Often outdated or politically skewed information |
| Parental Involvement | Balanced approach with review and opt-out provisions | Strict opt-in or opt-out measures that may curtail student exposure |
| Inclusivity | Focus on diversity, inclusivity, and non-stigmatizing language | Potential biases, including negative portrayals of certain groups |
This comparison makes it abundantly clear that for sexual education to truly benefit students, comprehensive, medically verified curricula must be made standard practice across jurisdictions.
Policy Recommendations and Future Perspectives
Given the present state of sexual education laws, a range of policy recommendations can help improve the current scenario for adolescents nationwide. Lawmakers, educational institutions, and parental groups all have roles to play in ensuring that young people receive essential, medically accurate information.
Some key recommendations include:
- Establishing National Guidelines: While education remains under state control, a set of national guidelines formulated by public health experts could serve as a benchmark. These guidelines would underscore the necessity for medically accurate and comprehensive instruction across all states.
- Enhanced Curriculum Review: States should implement routine reviews of sexual education curricula to ensure that all content remains up-to-date with current public health research. This process should involve independent experts and community stakeholders.
- Parental Involvement with Balance: Although allowing parents a say in the curriculum is important, policies must strike the right balance to avoid leaving students uneducated. Instead of blanket opt-out measures, states could consider more balanced approaches that encourage parental input without compromising educational quality.
- Training Educators Effectively: Teachers and administrators require ongoing training to handle the tricky parts of sexual education effectively. Their professional development should cover the fine points of health information, culturally sensitive language, and innovative educational techniques.
- Monitoring and Accountability: Independent bodies should be tasked with monitoring sexual education content and educator performance. These groups can help figure a path through the regulatory maze, ensuring that curricula adhere to both health guidelines and legal standards.
An effective policy framework based on these recommendations could lead to significant improvements in adolescent sexual health outcomes, reducing rates of STIs, unwanted pregnancies, and other related health issues. In many ways, such changes are not just important—they are essential to providing every student a must-have foundation for responsible decision-making.
Legal Challenges and Roadblocks Ahead
Despite the promising recommendations, significant legal challenges and political roadblocks remain. The existing state-level mandates are often loaded with problems, and reversing these long-held positions can be both intimidating and nerve-racking. Educational reform in this area is riddled with tension, as competing interests—including religious groups, political activists, and community organizations—hinder efforts to introduce comprehensive curricula.
Some of the most tricky parts in addressing these legal challenges include:
- Overcoming Political Resistance: In many states, changing sexual education mandates is on edge due to long-established political positions. The pushback is often not just about curriculum content, but about deeper cultural and ethical conflicts.
- Ensuring Uniformity in Diverse Regions: The variation in how sexual education is delivered in different parts of the country makes it difficult to implement universal standards. The authority to determine curriculum content remains a state prerogative, complicating any attempt at nationwide reform.
- Balancing Parental Rights and Educational Needs: The law must continuously find a balance between protecting parental rights and ensuring that all students receive the gnarly, evidence-based information they need to exercise sound judgment regarding their health.
These issues represent the subtle parts and hidden complexities that render sexual education reform a multi-layered problem. As lawmakers and educational leaders take a closer look at the current landscape, understanding these twists and turns will be key to crafting policies that are both fair and effective.
Conclusion: Toward a More Informed Future for American Youth
The current state of sexual education in the United States, characterized by a patchwork of inconsistent and politically influenced mandates, represents a significant challenge for the well-being of young people. With only a fraction of states mandating medically accurate instruction and a heavy reliance on abstinence-only messages, too many adolescents are left to figure a path through a tangle of outdated ideas and politically charged constraints.
For sexual education to be truly effective, lawmakers must work through the underlying legal dilemmas and reorient policies toward providing comprehensive and unbiased curricula that address the full range of sexual health topics. Public health experts, educators, and community stakeholders have the opportunity—and the responsibility—to advocate for reforms that ensure every student has access to clear, medically vetted, and inclusive information.
While the road to reform may seem overwhelming and filled with nerve-racking complications, the future of sexual education depends on addressing these challenges head-on. By recognizing the subtle details, managing your way through the little twists, and staying focused on the key priorities of public health and adolescent well-being, we can build a more informed and healthier future for all young Americans.
In this complex legal maze, every student deserves more than a politically motivated snapshot of sexual education. They deserve an approach that combines critical public health insights, balanced legal frameworks, and thoughtful policy-making—a must-have foundation that empowers them to make safe, informed decisions as they grow into adulthood.
Ultimately, the pursuit of effective sexual education is not just an educational issue, but a broader social imperative that touches on individual rights, public health, and legal accountability. By steering through the confusing bits and managing the tangled issues inherent in the current system, policymakers can help secure a future where every adolescent has the knowledge and confidence to navigate the challenges of sexual health responsibly.
It is time for a concerted effort by state legislators, educators, and community leaders to replace outdated mandates with dynamic, inclusive, and medically sound curricula. Only through a well-balanced blend of clear legal standards, thoughtful parental involvement policies, and comprehensive educational practices can we ensure that the next generation is fully equipped to meet the demands of their health and relationships head-on.
As we take a closer look at the state-by-state landscape of sexual education, let us remember that this issue goes beyond individual state lines; it is a national challenge, one that calls for courage, clarity, and continuous reflection on the responsibilities we bear toward our youth. Working together, we can resolve the on edge disputes and create an environment where every student has the key tools to protect their health and well-being, paving the way for a more informed, equitable future.
Originally Post From https://www.news-medical.net/news/20250822/Inconsistent-state-laws-undermine-sexual-education-across-the-United-States.aspx
Read more about this topic at
SIECUS Releases 2025 State Report Cards Update
Only 37% of US states require sexual education in schools ...








No comments:
Post a Comment